- Short Range Ultrasonic Testing (SRUT) is a non-destructive testing technique that utilizes high frequency ultrasonic waves to inspect localized areas of a component or structure.
- Short Range UT works based on the principle of sending high-frequency ultrasonic waves into the material and analyzing the reflected signals to detect defects. It involves using a small, handheld probe that emits and receives ultrasonic waves. The probe is placed directly on the surface of the component being inspected, allowing for localized and targeted inspection of specific areas. The received signals are analyzed to identify defects such as cracks, discontinuities, or wall thickness variations.
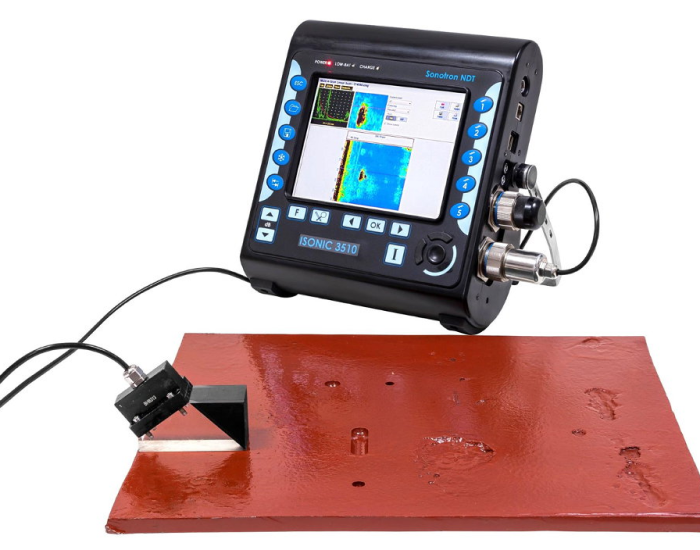




Application:
- Short Range UT is commonly used for the inspection of welds, pipes, tanks, and other components in various industries, including manufacturing, construction, oil and gas, and aerospace. It is particularly effective for inspecting areas that are difficult to access with conventional UT techniques, such as complex geometries, narrow gaps, or curved surfaces. Short Range UT can detect defects in localized regions, making it suitable for focused inspections and rapid defect identification.
Advantages:
- 1. Targeted Inspection: Short Range UT allows for localized inspection of specific areas, enabling targeted defect detection and analysis.
- 2. Easy to Use: The handheld nature of the probe makes Short Range UT easy to use and maneuver, even in areas with limited accessibility.
- 3. Rapid Inspection: Short Range UT provides quick inspection results, making it efficient for spot inspections and assessments.
- 4. Real-Time Feedback: The immediate feedback from the probe allows for real-time analysis of the inspection results.
- 5. Portable and Versatile: The portable nature of Short Range UT equipment makes it adaptable to various inspection scenarios and field applications.








Limitations:
- 1. Limited Inspection Range: Short Range UT is not suitable for inspecting large areas or performing full coverage inspections. It is best suited for localized inspections.
- 2. Surface Condition Dependency: The effectiveness of Short Range UT is dependent on the surface condition and coupling between the probe and the material being inspected. Rough or contaminated surfaces can affect the accuracy of the inspection.
- 3. Limited Depth Penetration: Short Range UT is typically used for near-surface defect detection and may have limitations in detecting defects deeper within the material.
- 4. Operator Skill: Proper training and expertise are required to correctly position and interpret the signals obtained from Short Range UT inspections.

