- Ultrasonic Testing is a volumetric Non-Destructive Testing (NDT) method. Unlike surface inspection methods, UT makes it possible to find flaws inside the material. Highfrequency sound waves are sent into the material with an ultrasonic transducer. The ultrasound that reflects off defects in the material is made visible in a graph. Ultrasonic Testing gives insight in the depth, size, nature and orientation of the detected indications. The thickness of the material, such as wall thickness of pipes, can also be measured.
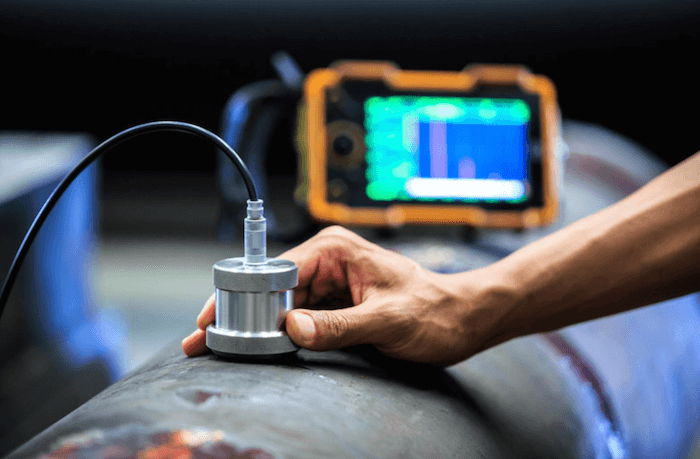



Advantages of Ultrasonic Testing:
- High penetrating power
- High sensitivity
- Usually only one surface needs to be accessible
- Insight in size, orientation, shape and nature of defectsYf
- Non-hazardous to operations or nearby personnel
- Portable equipment
- Can be used in automated setup
- Immediate test results
Limitations of Ultrasonic Testing:
- Surface must be accessible to transmit ultrasound
- Usually a couplant (gel or oil) is needed to enable interference-free transfer of the ultrasound
- Objects that have a rough surface or are very small, thin or not homogenous are difficult to inspect
- Cast iron and other coarse grained materials are difficult to inspect due to low sound transmission and high signal noise
- Linear flaws oriented parallel to the direction of the sound beam may go undetected
- Reference standards are required for equipment calibration and for the characterization of flaws